Westfield Students in the News for Gene Annotations
Head Start for Tomorrow’s Scientists
UB medical school project is changing students’ career ideas
From sheep to science: A Westfield success story
WACS students ‘doing real science’
Westfield student programs described
Selection of Gene Annotation Research Posters by Westfield Students
WACS students have been submitting posters to the University at Buffalo capstone poster symposium since 2010.
2015
Gene Annotation of Ksed_04940, a Putative Copper Chaperone Protein in Kytococcus sedentarius
Gene Annotation of Ksed_04890, a Hypothetical Protein of Unknown Function in Kytococcus sedentarius
2016
Annotation of the Kytococcus sedentarius Genome from DNA Coordinates 218553 to 218966
Annotation of the Kytococcus sedentarius Genome from DNA Coordinates 403939 to 414240
Gene Annotation of Ksed_02310, a Putative Fructosamine-3-Kinase in Kytococcus sedentarius
In 2017, Mr. Knappenberger started using DNA sequences from “Cryptids” as a way to introduce high school students to genomics.
An Investigation of reported Sasquatch (Homo sapiens cognatus) sequence M16.
Has Sasquatch (Homo sapiens cognatus) DNA been sequenced?
Testing a Sasquatch’s (Homo sapiens cognatus) gene AMEL_Y.
Research on a Reported Sasquatch (Homo sapien cognatus) gene HAR1
Research on Sasquatch (Homo sapiens cognatus) Gene MC1R.
2018
“Yeti” hair DNA sequence >MG131870.1 is actually from a Tibetan Blue Bear.
Geni-ACT.org
Guiding Education through Novel Investigation-Academic Collaboration Toolkit
A complete Gene annotation for KSED RS00005 gene on Google docs. https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&pid=sites&srcid=ZGVmYXVsdGRvbWFpbnx1YmJjbHNnZW5vbWVhbm5vdGF0aW9ufGd4OjE2M2E5NmE5Yjg4YjNhYw
>Sample Gene from Chlamydia trachomatis
ATGACAGAGTCATATGTAAACAAAGAAGAAATCATCTCTTTAGCAAAGAA
TGCTGCATTGGAGTTGGAAGATGCCCACGTGGAAGAGTTCGTAACATCTA
TGAATGACGTCATTGCTTTAATGCAGGAAGTAATCGCGATAGATATTTCG
GATATCATTCTTGAAGCTACAGTGCATCATTTCGTTGGTCCAGAGGATCT
TAGAGAAGACATGGTGACTTCGGATTTTACTCAAGAAGAATTTTTATCTA
ACGTTCCCGTGTCGTTGGGAGGATTAGTCAAAGTCCCTACAGTTATCAAA
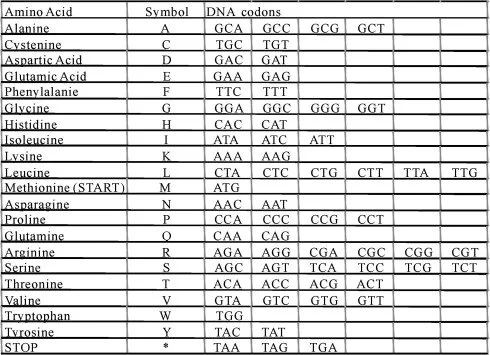
TAG3 letters are called a codon. Each codon codes for an amino acid. The amino acids form a protein, which serves a specific purpose.
Scientists have given each amino acid a one letter code.
>amino acid sequence of the above Chlamydia trachomatis gene
MTESYVNKEEIISLAKNAALELEDAHVEEFVTSMNDVIALMQEVIAIDIS
DIILEATVHHFVGPEDLREDMVTSDFTQEEFLSNVPVSLGGLVKVPTVIKConvert DNA sequence to Amino Acid Sequence.
Amino acids also have chemical properties, such as polar, neutral, basic, acidic, or hydrophobic.
Polar Amino Acid-able to participate in hydrogen bonding. Hydrophilic. Glycine (G), Serine (S), Threonine (T), Tyrosine (Y) and Cysteine (C).
Neutral Polar Amino acid.- amide side chain do NOT produce basic solutions. , proton donor or proton acceptor, Hydrophilic, Asparagine (N) and glutamine (Q)
Basic Amino acid -Polar, Raise pH., Hydrophilic, nitrogen side chains, proton acceptor, form positive charges. Lysine (K), Arginine (R) and Histidine (H).
Acidic Amino acid-Polar, lower pH, Hydrophilic, Carboxylic side chain, proton donor, form negative charges. Aspartic Acid (D) and Glutamic acid (E).
Hydrophobic amino acid-”water Fearing” found buried in the core of a protein. side chains composed mostly of carbon and hydrogen. Alanine (A) , Isoleucine ( I), Leucine (L), Methionine (M ), Phenylalanine ( F), Valine (V), Proline ( P) and
Glycine (G).
ATG -Methionine (M) Start Codon
ACA-Threonine (T) polar amino acid. GAG-Glutamic Acid (E) Acidic amino acid TCA-Serine (S) Polar Amino AcidTAT-Tyrosine (Y) Polar Amino acidGTA-Valine (V) Hydrophobic (water fearing)AAC-Asparagine (N) Neutral amino acidAAA -Lysine (K)-Basic amino acidGAA- Glutamic acid (E)-Acidic amino acid GAA-Glutamic Acid (E)-Acidic amino acidATC -Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic amino acidATC-Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic amino acid. TCT-Serine (S) Polar amino acidTTA-Leucine (L) HydrophobicGCA-Alanine (A) HydrophobicAAG-Lysine (K) BasicAAT-Asparagine (N) Neutral
GCT-Alanine (A) Hydrophobic GCA-Alanine (A)Hydrophobic TTG-Leucine (L) Hydrophobic GAG-Glutamic acid (E) Acidic TTG-Leucine (L) Hydrophobic GAA -Glutamic acid (E) Acidic GAT-Aspartic acid (D) Acidic GCC- Alanine (A) Hydrophobic CAC - Histidine (H) BasicGTG -Valine (V) Hydrophobic GAA- Glutamic Acid (E) Acidic
GAG-Glutamic Acid (E) Acidic TTC-Phenylalanine (F) Hydrophobic GTA-Valine (V)Hydrophobic ACA-Threonine (T) PolarTCT-Serine (S) Polar
ATG -Methionine (M) Hydrophobic AAT- Asparagine (N) NeutralGAC-Aspartic Acid (D) Acidic GTC-Valine (V) Hydrophobic ATT-Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic GCT -Alanine (A) Hydrophobic TTA -Leucine (L) Hydrophobic ATG -Methionine(M) Hydrophobic CAG-Glutamine (Q) NeutralGAA-Glutamic acid (E) Acidic GTA-Valine (V) Hydrophobic ATC-Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic GCG-Alanine (A) Hydrophobic ATA -Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic GAT -Aspartic Acid (D) Acidic ATT -Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic TCG -Serine (S) Polar
GAT Aspartic Acid (D) Acidic ATC Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic ATT -Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic CTT -Leucine (L) Hydrophobic GAA - Glutamic acid (E) Acidic GCT -Alanine (A) Hydrophobic ACA-Threonine (T) PolarGTG-Valine (V) Hydrophobic CAT' -Histidine (H) Basic CAT -Histidine (H) BasicTTC-Phenylalanine (F) HydrophobicGTT-Valine (V) HydrophobicGGT-Glycine (G) PolarCCA-Proline (P) HydrophobicGAG-Glutamic Acid (E) Acidic GAT-Aspartic Acid (D)Acidic CTT-Leucine (L) Hydrophobic
AGA-Arginine (R) BasicGAA-Glutamic acid (E) AcidicGAC-Aspartic Acid (D) Acidic ATG-Methionine (M) Hydrophobic GTG-Valine (V) Hydrophobic ACT-Threonine (T) PolarTCG-Serine (S) PolarGAT-Aspartic acid (D) Acidic TTT-Phenylalanine (F) Hydrophobic ACT-Threonine (T) PolarCAA-Glutamine (Q) Neutral GAA-Glutamic acid (E) Acidic You may try completing the rest.
GAA- _________TTT- _________TTA- _________TCT- _________AAC- _________
GTT- __________CCC- __________GTG- ___________TCG- ___________TTG -____________GGA Glycine (G) PolarGGA-Glycine (G) PolarTTA -Leucine (L) Hydrophobic GTC-Valine (V) Hydrophobic AAA-Lysine (K) Basic GTC -Valine (V) Hydrophobic CCT -Proline (P) Hydrophobic ACA-Threonine (T) PolarGTT Valine (V) Hydrophobic ATC -Isoleucine (I) Hydrophobic AAA-Lysine (K) Basic
TAG-STOP Codon *
What would this protein look like?
Important Information
Basic DNA YouTube Videos
What is DNA and How Does it Work?
Module 1: Basic Information
The Locus Tag, Sequence Coordinates, DNA Sequences DNA Sequence Length, Amino acid sequence and Amino acid sequence length for his/her gene will be added to your gene notebook.
Module 2: Sequence-based Similarity Data Module
It answers the question: Is the protein you are annotating similar to other known proteins? This involves pasting the sequence into websites and learning how to interpret the results.
BLAST finds regions of similarity between biological sequences. The program compares nucleotide or protein sequences to sequence databases and calculates the statistical significance.
CDD (Conserved Domain Database) is a protein annotation resource that consists of a collection of well-annotated multiple sequence alignment models for ancient domains and full-length proteins.
T-Coffee Multiple Sequence Alignment
T-Coffee is a multiple sequence alignment program.
WebLogo is a web based application designed to make the generation of sequence logos as easy and painless as possible.
What do the colors mean?
BLACK-Hydrophobic A,V, L, I P, W, F & M.
RED-Acidic D&,E
BLUE-Basic K,R, & H.
GREEN -Polar G, S, T, Y & C.
PURPLE- Neutral Q & N
N-Terminus=(also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide.
C-Terminus-(also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain protein orpolypepotide), terminated by a free carboxyl (-COOH).
Interpretation: This WebLogo is more conserved at the C- terminus than the N-terminus. .
Module 3. Structure-based Evidence Module:
Is the protein you are annotating functionally similar to other known proteins?
TIGR FAMS supports searches of protein sequence against a database of hidden Markov models (HMMs) based upon protein families.
The Pfam database is a large collection of protein families, each represented by multiple sequence alignments and hidden Markov models (HMMs).
The Vision of the PDB is to enable open access to the accumulating knowledge of 3D structure, function, and evolution of biological macromolecules, expanding the frontiers of fundamental biology, biomedicine, and biotechnology.
Module 4. Cellular Localization:
Is the protein you are annotating located in the cytoplasm of the cell, embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane or secreted?
Prediction of transmembrane helices in proteins
TMHMM is a method for prediction transmembrane helices based on a hidden Markov model
The SignalP 5.0 server predicts the presence of signal peptides and the location of their cleavage sites in proteins from Archaea, Gram-positive Bacteria, Gram-negative Bacteria and Eukarya.
Predict lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-negative Eubacteria
Phobius: A combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide predictor
PsortB: most precise bacterial localization prediction tool available.
Module 6: Enzymatic Function.
Is the protein you are annotating an enzyme, if so, what is its function?
KEGG PATHWAY is a collection of manually drawn pathway maps representing our knowledge on the molecular interaction, reaction and relation networks for:
1. Metabolism
2. Genetic Information Processing
3. Environmental Information Processing
4. Cellular Processes
5. Organismal Systems
6. Human Diseases
7. Drug Development
MetaCyc is a curated database of experimentally elucidated metabolic pathways from all domains of life.
ENZYME is a repository of information relative to the nomenclature of enzymes.
Module 8: Horizontal Gene Transfer
Did the bacteria get the gene from another organism?
Module 5: Alternative Open reeading Frame
Did the gene caller call the start codon correctly?
If not, what is the correct start codon?
Vocabulary:
Shine-Dalgarno sequence- (5′-AGGAGGU-3′) ribosomal binding site in bacterial messenger RNA , generally located around 8 bases upstream of the start codon.

Get Involved
Register to participate or donate